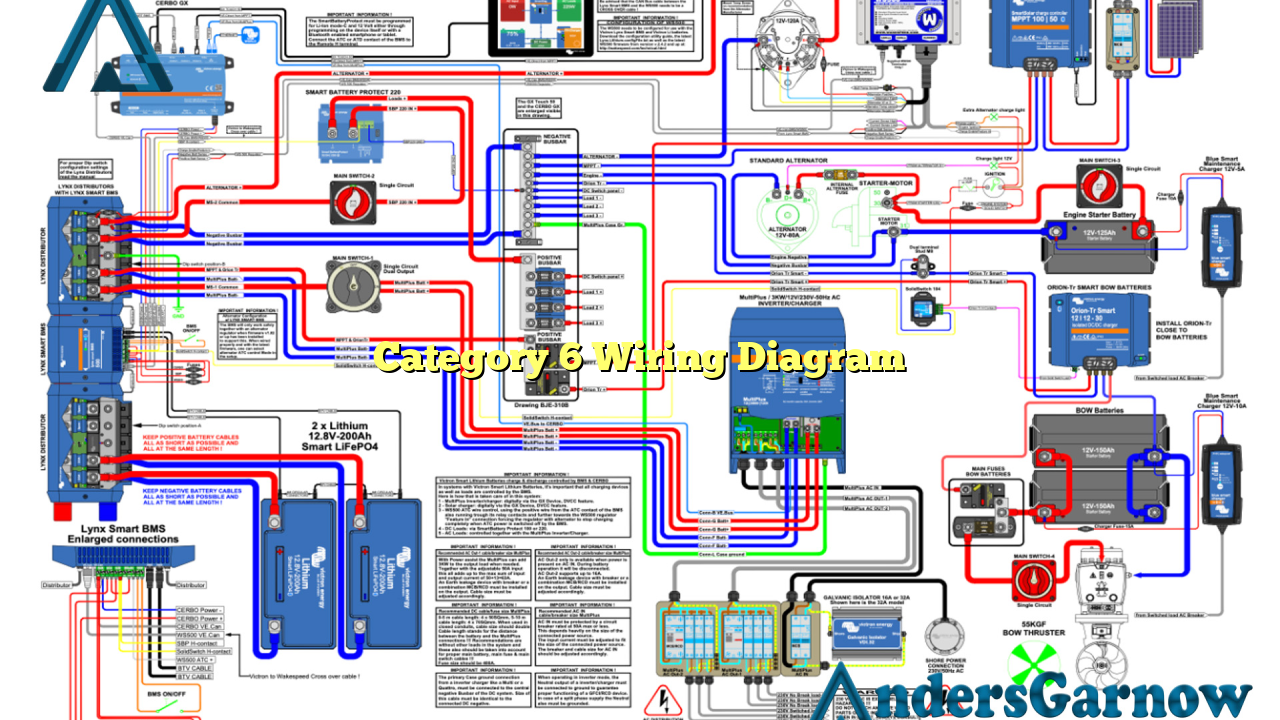
Hello readers,
Welcome to this informative article about Category 6 wiring diagram. In this article, we will explore the details of Category 6 wiring diagram, its advantages and disadvantages, as well as alternative options available. So, let’s dive right in!
1. What is Category 6 Wiring Diagram?
Category 6 wiring diagram, also known as Cat 6, is a standardized twisted pair cable for Ethernet and other network physical layers. It is an enhanced version of the Category 5 cable and provides higher bandwidth and faster data transmission rates.
2. Advantages of Category 6 Wiring Diagram
Category 6 wiring diagram offers several advantages over its predecessors:
- Higher Bandwidth: Cat 6 cables can support bandwidths up to 250 MHz, allowing for faster data transmission.
- Faster Data Transmission: With improved signal-to-noise ratio, Cat 6 cables provide faster data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- Reduced Crosstalk: Category 6 cables are designed with tighter twists and better insulation, minimizing crosstalk between wires and improving overall signal quality.
- Backward Compatibility: Cat 6 cables are backward compatible with previous versions, such as Cat 5 and Cat 5e, allowing for easy integration into existing network infrastructures.
- Future-proofing: Installing Cat 6 cables ensures compatibility with future network technologies and upgrades.
3. Disadvantages of Category 6 Wiring Diagram
While Cat 6 wiring diagram offers numerous benefits, it also has a few downsides:
- Cost: Cat 6 cables are generally more expensive compared to earlier versions. However, the price difference has significantly decreased in recent years.
- Installation Complexity: Due to its tighter twists, Cat 6 cables require more careful installation to maintain performance standards. Improper installation can result in reduced signal quality.
4. Alternative Options
Aside from Cat 6, there are alternative options available for network wiring:
- Category 5e (Cat 5e): This is an enhanced version of Cat 5 and offers similar performance to Cat 6 at a lower cost. It is suitable for most residential and small office applications.
- Category 7 (Cat 7): Cat 7 cables provide even higher bandwidth and better shielding compared to Cat 6. They are typically used in data centers and other high-performance environments.
- Fiber Optic Cables: Fiber optic cables offer the highest performance and bandwidth but are more expensive and require specialized equipment for installation.
5. Category 6 Wiring Diagram Details
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cable | Four twisted pairs of copper wires with an overall sheath |
| Connectors | RJ-45 connectors are commonly used for terminating Cat 6 cables |
| Color Coding | T568A or T568B wiring standards are used for pin assignments |
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I use Cat 6 cables for telephone connections?
A: Yes, Cat 6 cables can be used for telephone connections, as they are backward compatible with Cat 3 and Cat 5e cables.
Q: Can I mix Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables in the same network?
A: It is generally recommended to use the same cable type throughout the network to maintain consistent performance. However, Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables are compatible with each other.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Category 6 wiring diagram is a reliable and high-performance solution for network installations. It offers higher bandwidth, faster data transmission, and reduced crosstalk. While it may have some drawbacks, such as installation complexity and cost, the benefits outweigh the disadvantages. Consider your specific requirements and budget when choosing the right network wiring option for your needs.