Hello readers,
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on schematic drawing, a powerful tool that is widely used in various industries. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of schematic drawing, its benefits, drawbacks, and alternative options. So, let’s dive right in!
1. What is Schematic Drawing?
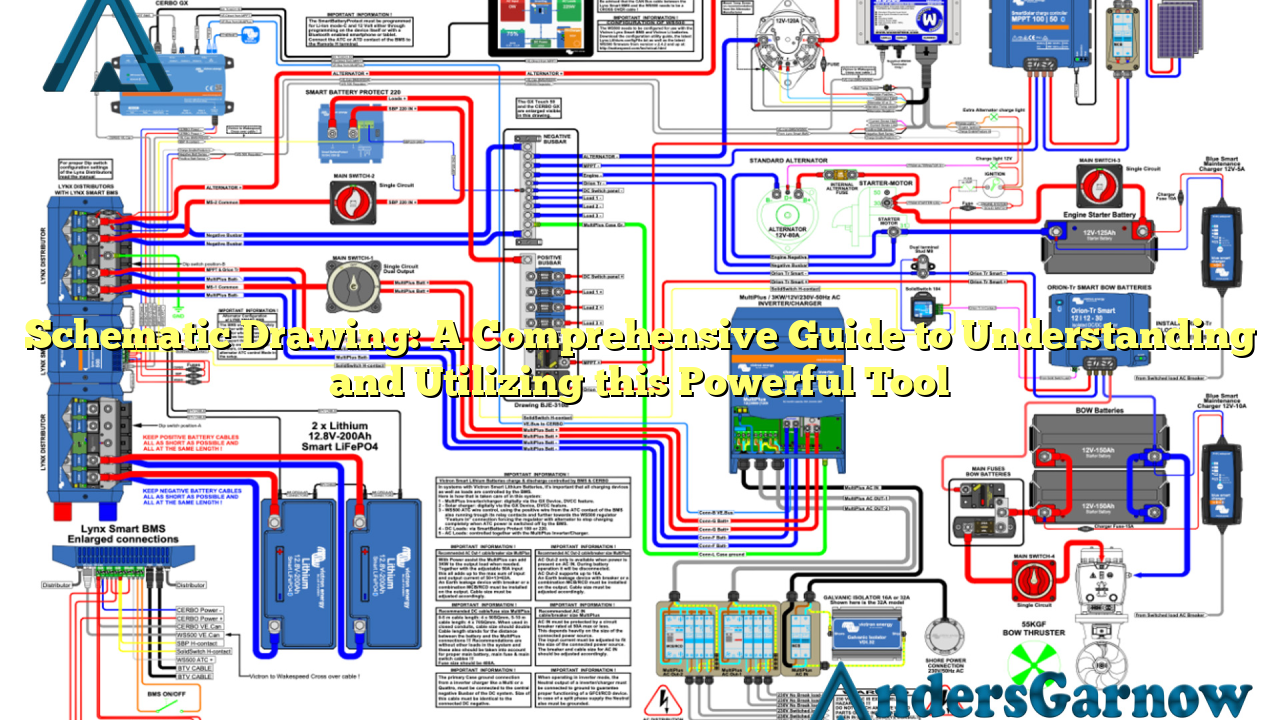
Schematic drawing is a visual representation of a system or process using symbols, lines, and diagrams. It is commonly used in engineering, electronics, architecture, and other fields to illustrate the connections and relationships between different components or elements.
The main purpose of schematic drawing is to simplify complex concepts and ideas, making them easier to understand and communicate. By using standardized symbols and conventions, schematic drawings enable professionals to convey information quickly and accurately.
Advantages of Schematic Drawing:
| Advantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Clarity and Simplicity | Schematic drawings provide a clear and simplified representation of complex systems, making it easier for professionals to understand and analyze. |
| 2. Easy Communication | By using standardized symbols and conventions, schematic drawings facilitate effective communication among professionals from different disciplines. |
| 3. Time and Cost Efficiency | Schematic drawings help in identifying design flaws and potential issues early in the process, saving time and reducing costs in the long run. |
| 4. Scalability | Schematic drawings can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate changes or modifications in the system, allowing for flexibility. |
Disadvantages of Schematic Drawing:
While schematic drawing offers numerous benefits, it also has some limitations. It is important to consider these drawbacks before utilizing schematic drawing in your projects:
- 1. Lack of Realism: Schematic drawings may not accurately represent the physical appearance or dimensions of the system, leading to potential misconceptions.
- 2. Limited Detail: Due to the simplified nature of schematic drawings, they may not provide a comprehensive level of detail, particularly for complex systems.
- 3. Interpretation Challenges: Schematic drawings require the viewer to have a certain level of technical knowledge and understanding to interpret the symbols correctly.
2. The Key Elements of Schematic Drawing
In order to create and interpret schematic drawings effectively, it is essential to understand the key elements involved:
- 1. Symbols: Schematic drawings utilize standardized symbols to represent various components, such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and more. These symbols provide a concise way to convey information.
- 2. Lines: Different types of lines are used in schematic drawings to depict connections, paths, and relationships between components. For example, solid lines represent conductive pathways, while dashed lines indicate indirect connections.
- 3. Labels: Labels and annotations are added to the schematic drawings to provide additional information about specific components or connections, ensuring clarity and understanding.
3. Alternatives to Schematic Drawing
While schematic drawing is widely used and highly effective in many cases, there are alternative approaches that can be considered depending on the specific requirements of your project:
- 1. 3D Modeling: For projects that require a more realistic representation of the system, 3D modeling tools can be utilized to create detailed visualizations.
- 2. Flowcharts: In situations where the emphasis is on illustrating the flow of processes or decision-making, flowcharts can be a suitable alternative to schematic drawings.
- 3. Circuit Simulation Software: When working with complex electrical systems, circuit simulation software can provide a virtual environment for testing and analyzing circuits without the need for physical prototypes.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some commonly asked questions about schematic drawing:
Q: Can schematic drawings be used for architectural purposes?
A: While schematic drawings are primarily used in engineering and electronics, they can also be utilized in architecture to represent the basic layout and connections of a building’s systems.
Q: Is it necessary to learn specific software for creating schematic drawings?
A: There are various software options available for creating schematic drawings, such as AutoCAD, Eagle, and KiCad. Learning a specific software can enhance your productivity and enable you to create professional-looking drawings.
Q: Can schematic drawings be easily modified or updated?
A: Yes, one of the advantages of schematic drawings is their flexibility. They can be easily modified or updated to accommodate changes in the system design or components.
Conclusion
Schematic drawing is a powerful tool that simplifies complex systems and processes, allowing professionals to convey information effectively. While it has its advantages and disadvantages, understanding the key elements and considering alternative options can help you make informed decisions in your projects. Whether you are an engineer, architect, or electronics enthusiast, mastering schematic drawing can greatly enhance your ability to communicate and visualize ideas.
Thank you for reading our comprehensive guide on schematic drawing. We hope you found it informative and useful!