Hello readers! In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of schematic drawings. Whether you are a professional engineer, an aspiring designer, or simply curious about the subject, we will explore the various aspects of schematic drawings, their advantages, disadvantages, and alternative options. So, let’s get started!
1. What are Schematic Drawings?
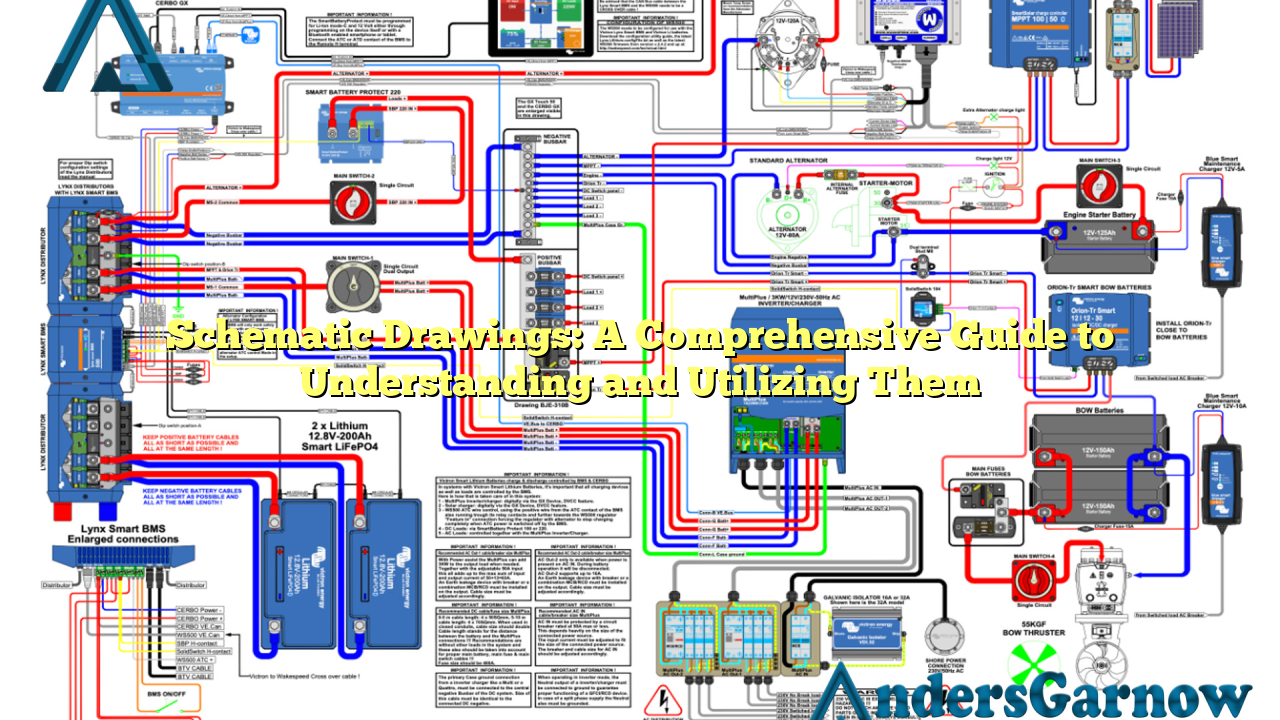
Schematic drawings, also known as schematic diagrams or schematics, are visual representations of a system or process using symbols and lines to convey information. They are widely used in engineering, electronics, architecture, and various other fields to illustrate the relationships between different components and their functions.
2. Advantages of Schematic Drawings
Schematic drawings offer several advantages that make them indispensable in many industries. Firstly, they provide a clear and concise overview of complex systems, making it easier for professionals to understand and analyze them. These drawings also facilitate effective communication, as they can be universally understood regardless of language barriers.
Furthermore, schematic drawings allow for easy identification of faulty components or areas in need of improvement. They serve as valuable documentation for troubleshooting and maintenance purposes, saving time and effort in the long run. Additionally, schematics aid in the design and development of new systems by providing a blueprint to follow.
3. Disadvantages of Schematic Drawings
While schematic drawings have numerous benefits, they are not without their limitations. One of the main drawbacks is their complexity, especially in intricate systems. Interpreting intricate schematics requires expertise and experience, which can pose challenges for beginners or those unfamiliar with the specific symbols used.
Another disadvantage of schematic drawings is their static nature. As they represent a specific moment in time, any changes or modifications to the system may render the schematic inaccurate. Updating schematics can be time-consuming, particularly if the changes are extensive.
4. Alternatives to Schematic Drawings
Although schematic drawings are widely used, alternative methods exist for visualizing systems and processes. One such alternative is 3D modeling, which provides a more realistic representation of the system. With 3D models, users can explore the system from various angles and perspectives, gaining a deeper understanding of its spatial layout.
Another option is flowcharts, which are particularly useful for illustrating sequential processes. Flowcharts use different shapes and arrows to show the flow of information or materials through a system. They are often used in programming, software development, and business process management.
5. Schematic Drawings vs. 3D Modeling
While 3D modeling offers advantages in terms of visual realism, schematic drawings excel in their simplicity and ease of interpretation. 3D models may be overwhelming for those not well-versed in the field, whereas schematics provide a more accessible representation. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements and preferences of the intended audience.
6. Schematic Drawings vs. Flowcharts
Similarly, the choice between schematic drawings and flowcharts depends on the nature of the system or process being depicted. Schematic drawings are suitable for showcasing intricate relationships between components, while flowcharts are more effective in illustrating sequential processes or decision trees. Selecting the appropriate visual representation ensures clear and effective communication.
7. Schematic Drawings in the Engineering Field
In the engineering field, schematic drawings play a crucial role in the design, construction, and maintenance of various systems. From electrical circuits and mechanical assemblies to plumbing layouts and HVAC systems, engineers rely on schematics to understand and communicate the intricacies of their designs. Schematics aid in troubleshooting, repairs, and modifications throughout the lifespan of a system.
8. Schematic Drawings in the Architecture Field
In architecture, schematic drawings serve as a starting point for designing buildings and structures. They outline the basic spatial relationships, circulation patterns, and functional layouts of a project. Architects use schematics to communicate their design concepts to clients, consultants, and contractors, ensuring a shared understanding of the project’s vision.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Schematic Drawings
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. What software can I use to create schematic drawings? | Popular software options include AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Eagle, and Altium Designer. Choose a software that best suits your specific needs and skill level. |
| 2. Can I learn to interpret schematic drawings on my own? | While it is possible to learn schematic interpretation independently, it is recommended to seek guidance from professionals or enroll in relevant courses to accelerate the learning process. |
| 3. How often should schematic drawings be updated? | Schematic drawings should be updated whenever there are significant changes or modifications to the system. Regular reviews and updates are essential to ensure accuracy and reliability. |
| 4. Are there any international standards for schematic symbols? | Yes, several international standards exist, such as the IEC 60617 for electrical symbols and the ANSI/IEEE Std 315 for logic symbols. These standards promote consistency and universal understanding. |
In Conclusion
Schematic drawings are invaluable tools for understanding, designing, and maintaining complex systems. Despite their limitations, their advantages outweigh the drawbacks, making them indispensable in various industries. Whether you are an engineer, architect, or enthusiast, harnessing the power of schematic drawings can enhance your understanding and communication within your respective field. Remember, clear and concise visuals pave the way for efficient problem-solving and innovation!