Hello and welcome to our comprehensive guide on solenoid wiring diagrams. In this article, we will discuss the various aspects of solenoid wiring diagrams, including their purpose, components, advantages, disadvantages, and provide alternative options. So, let’s dive in!
1. Understanding Solenoid Wiring Diagrams
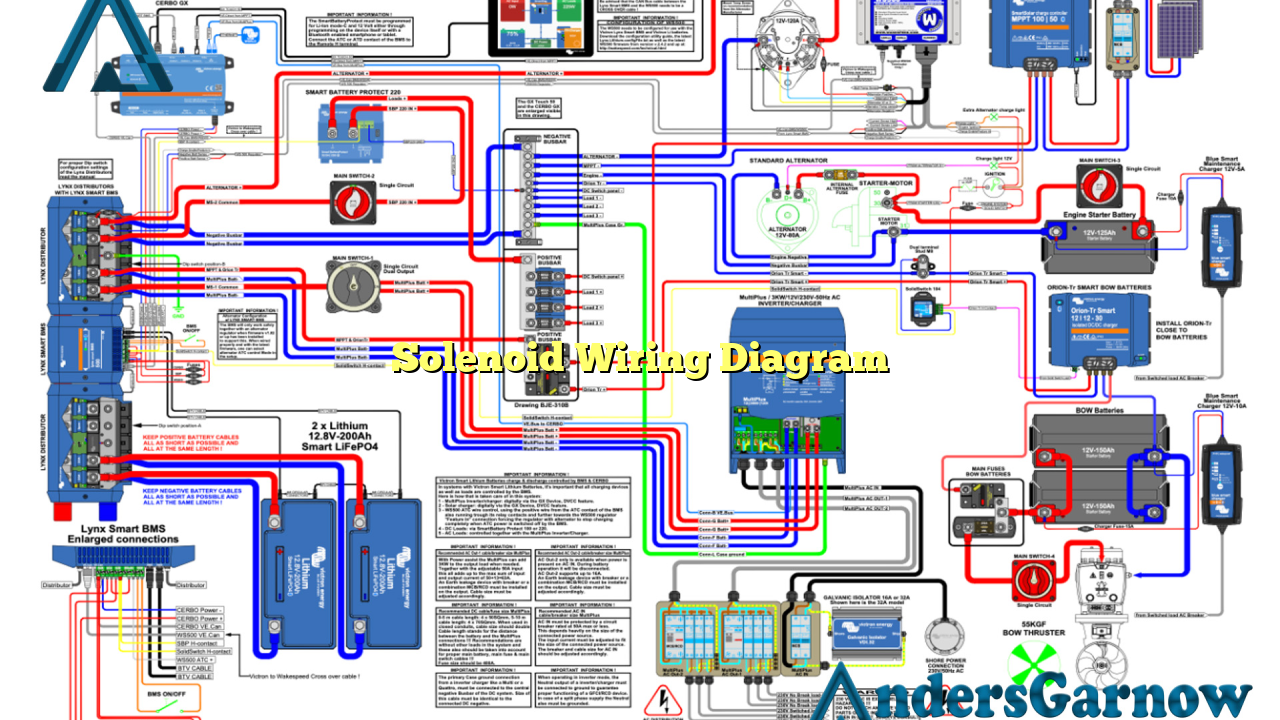
Solenoid wiring diagrams are graphical representations of the electrical connections and circuits involved in the functioning of solenoids. Solenoids are electromagnetic devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. They are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including automotive systems, industrial machinery, and home appliances.
Advantages of Solenoid Wiring Diagrams:
- Clear Visual Representation: Solenoid wiring diagrams provide a clear visual representation of the electrical connections, making it easier for technicians to understand and troubleshoot any issues.
- Standardization: These diagrams follow standardized symbols and conventions, ensuring consistency and ease of interpretation across different industries and applications.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: With a solenoid wiring diagram, technicians can quickly identify faulty connections, short circuits, or other electrical problems, minimizing downtime and reducing repair costs.
Disadvantages of Solenoid Wiring Diagrams:
- Complexity: Solenoid wiring diagrams can be complex, especially for individuals with limited electrical knowledge. Understanding the symbols and connections requires some level of expertise.
- Specificity: Each solenoid wiring diagram is specific to the particular application or system it represents. This means that a diagram designed for one solenoid may not be applicable to another, requiring customized diagrams for different scenarios.
- Upkeep and Updates: As technology advances and systems evolve, solenoid wiring diagrams may become outdated. Regular updates and modifications are necessary to ensure accuracy and relevancy.
2. Components of a Solenoid Wiring Diagram
A typical solenoid wiring diagram consists of the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Source | The source of electrical energy that powers the solenoid. |
| Switches | Devices that control the flow of electrical current to the solenoid. |
| Solenoid Coil | The coil responsible for generating the electromagnetic field. |
| Contacts | Physical connections that allow the current to flow through the solenoid. |
| Load | The device or mechanism that the solenoid operates. |
3. Alternatives to Solenoid Wiring Diagrams
While solenoid wiring diagrams are commonly used, there are alternatives available for specific applications. Some alternatives include:
- Relay Wiring Diagrams: Relays perform similar functions to solenoids and can be used as alternatives in certain circuits.
- Microcontroller-Based Systems: In modern applications, microcontrollers are often used to control solenoids, eliminating the need for traditional wiring diagrams.
FAQ
Q: Can I use a solenoid wiring diagram for different solenoids?
A: Solenoid wiring diagrams are specific to the solenoid and its application. Using a diagram designed for one solenoid may lead to incorrect connections or malfunction.
Q: Are solenoid wiring diagrams applicable to all industries?
A: Solenoid wiring diagrams are applicable to various industries, including automotive, industrial, and home appliances. However, specific diagrams may be required for different applications within these industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solenoid wiring diagrams are essential tools for understanding and troubleshooting the electrical connections in solenoid-operated systems. While they offer clear visual representations and standardized conventions, they can be complex and require expertise to interpret. It’s important to keep in mind the advantages and disadvantages of solenoid wiring diagrams and explore alternative options when necessary. By understanding the components and functions of solenoid wiring diagrams, technicians can ensure efficient and reliable operation of solenoid-based systems.